References: 1. XARELTO® [prescribing information]. Titusville, NJ: Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc. 2. Pradaxa® [prescribing information]. Ridgefield, CT: Boehringer lngelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc.; 2023. 3. Male C, Lensing AWA, Palumbo JS, et al; EINSTEIN-Jr Phase 3 Investigators. Rivaroxaban compared with standard anticoagulants for the treatment of acute venous thromboembolism in children: a randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Haematol. 2020;7(1):e18-e27. 4. ClinicalTrials.gov. NCT01895777. Open label study comparing efficacy and safety of dabigatran etexilate to standard of care in paediatric patients with venous thromboembolism (VTE). Accessed August 19, 2024. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT01895777 5. ClinicalTrials.gov. NCT02464969. Apixaban for the acute treatment of venous thromboembolism in children. Accessed August 19, 2024. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/
NCT02464969 6. ClinicalTrials.gov. NCT02798471. Hokusai study in pediatric patients with confirmed venous thromboembolism (VTE). Accessed August 19, 2024. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02798471 7. Lensing AWA, Male C, Young G, et al. Rivaroxaban versus standard anticoagulation for acute venous thromboembolism in childhood. Design of the EINSTEIN-Jr phase III study. Thromb J. 2018;16:34.
EINSTEIN-Jr clinical trial
The largest pediatric DOAC trial conducted for the treatment
of VTE and the first to evaluate a liquid formulation in this population1-6
A randomized, multicenter, active-controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial to evaluate XARELTO® vs comparator for treatment of acute VTE in a pediatric population3,7
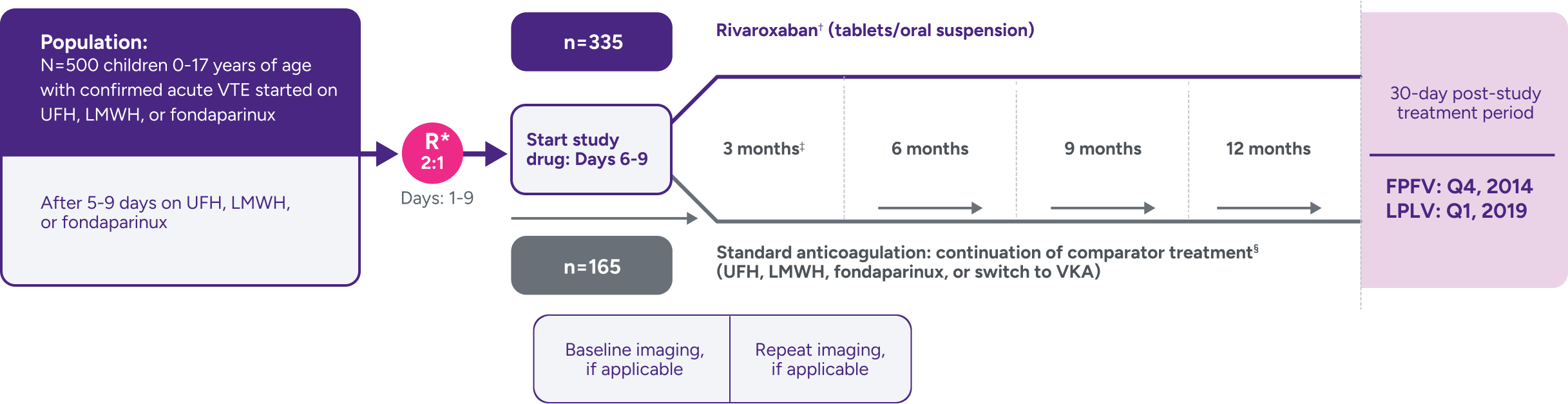
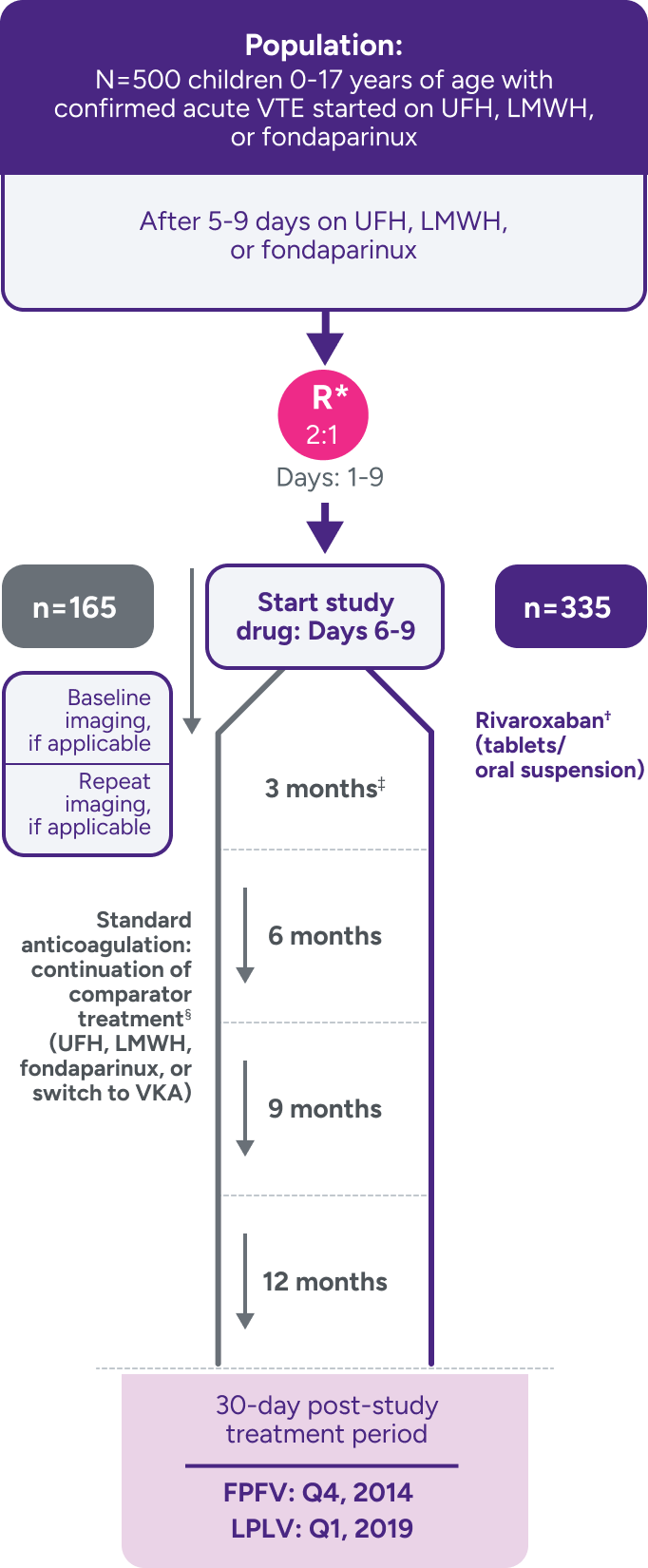
Not powered for noninferiority‖ due to the low incidence of VTE in children and the lack of well-documented information on recurrence and treatment effect with standard anticoagulants in children; hence, there was no formal a priori sample size calculation.3
Efficacy outcomes
Primary: symptomatic recurrent VTE in ITT population
Secondary: composite of recurrent VTE and deterioration on repeated vascular (clot) imaging
Principal safety outcome
Composite of major bleeding and clinically relevant nonmajor bleeding¶
*Stratified by age and by VTE site.
†Bodyweight-adjusted rivaroxaban dose equivalent to 20-mg once-daily adult dose.
‡Children aged <2 years with CVC-VTE: extension with maximum 2 blocks of 1 month, maximum duration of 3 months; decision to stop or continue treatment made after each 3- or 1-month block.
§
Comparators were given at therapeutic doses, according to international guidelines, and included UFH, LMWH, or fondaparinux. Following completion of 5 to 9 days of standard anticoagulation, participants continued with heparin treatment or were switched to a VKA at the discretion of the treating physician for a main study treatment period of 3 months (or 1 month for children <2 years with CVC-VTE). A diagnostic imaging test was obtained at baseline and at the end of the main study treatment. When clinically necessary, treatment was extended up to 12 months in total (or up to 3 months in total for children <2 years with CVC-VTE).1,3,7
||The study could not be powered to independently show noninferiority for efficacy of rivaroxaban in comparison to standard therapy in children; therefore, interpretation of the results relies in part on extrapolation of data obtained with rivaroxaban in adults. Hence, there was no formal a priori sample size calculation.
¶Clinically relevant nonmajor bleeding is clinically overt bleeding, which did not meet the criteria for major bleeding but was associated with medical intervention, unscheduled contact with a physician, temporary cessation of treatment, discomfort for the patient, or impairment of activities of daily life. Major bleeding is clinically overt bleeding associated with a decrease in hemoglobin of ≥2 g/dL, a transfusion of ≥2 units of packed red blood cells or whole blood, or bleeding at a critical site or with a fatal outcome.
CVC-VTE = central venous catheter–related venous thromboembolism; DOAC = direct oral anticoagulant; FPFV = first patient first visit; ITT = intent-to-treat; LMWH = low-molecular-weight heparin; LPLV = last patient last visit; R = randomization; UFH = unfractionated heparin; VKA = vitamin K antagonist; VTE = venous thromboembolism.
EINSTEIN-Jr clinical trial
The principal safety outcome was major and clinically relevant nonmajor bleeding1*†‡
Principal safety outcome
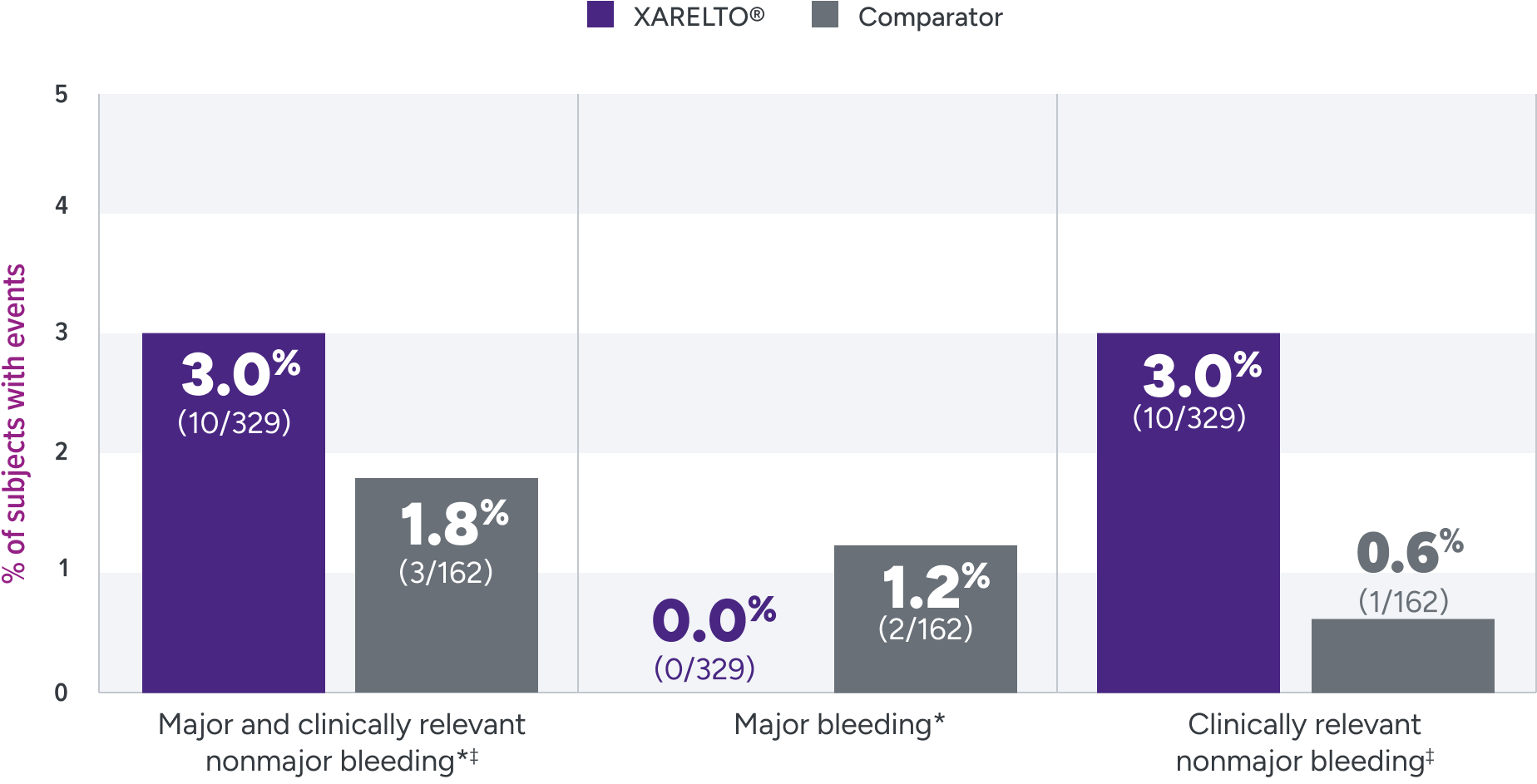
Not powered for noninferiority§ due to the low incidence of VTE in children and the lack of well-documented information on recurrence and treatment effect with standard anticoagulants in children; hence, there was no formal a priori sample size calculation.3
*Major bleeding is clinically overt bleeding associated with a decrease in hemoglobin of ≥2 g/dL, a transfusion of ≥2 units of packed red blood cells or whole blood, bleeding at a critical site, or bleeding at a critical site or with a fatal outcome.
†
Comparators were given at therapeutic doses, according to international guidelines, and included UFH, LMWH, or fondaparinux. Following completion of 5 to 9 days of standard anticoagulation, participants continued with heparin treatment or were switched to a VKA at the discretion of the treating physician for a main study treatment period of 3 months (or 1 month for children <2 years with CVC-VTE). A diagnostic imaging test was obtained at baseline and at the end of the main study treatment. When clinically necessary, treatment was extended up to 12 months in total (or up to 3 months in total for children <2 years with CVC-VTE).1,3,7
‡Clinically relevant nonmajor bleeding is clinically overt bleeding, which did not meet the criteria for major bleeding but was associated with medical intervention, unscheduled contact with a physician, temporary cessation of treatment, discomfort for the patient, or impairment of activities of daily life.
§The study could not be powered to independently show noninferiority for efficacy of rivaroxaban in comparison to standard therapy in children; therefore, interpretation of the results relies in part on extrapolation of data obtained with rivaroxaban in adults; hence, there was no formal a priori sample size.
CVC-VTE = central venous catheter-related venous thromboembolism; LMWH = low-molecular-weight heparin; UFH = unfractionated heparin; VKA = vitamin K antagonist; VTE = venous thromboembolism.
The EINSTEIN-Jr clinical trial was not powered for efficacy
Rates of recurrent DVT/PE were 1.2% with XARELTO® vs
3.0% with the comparator3*
Primary efficacy outcome
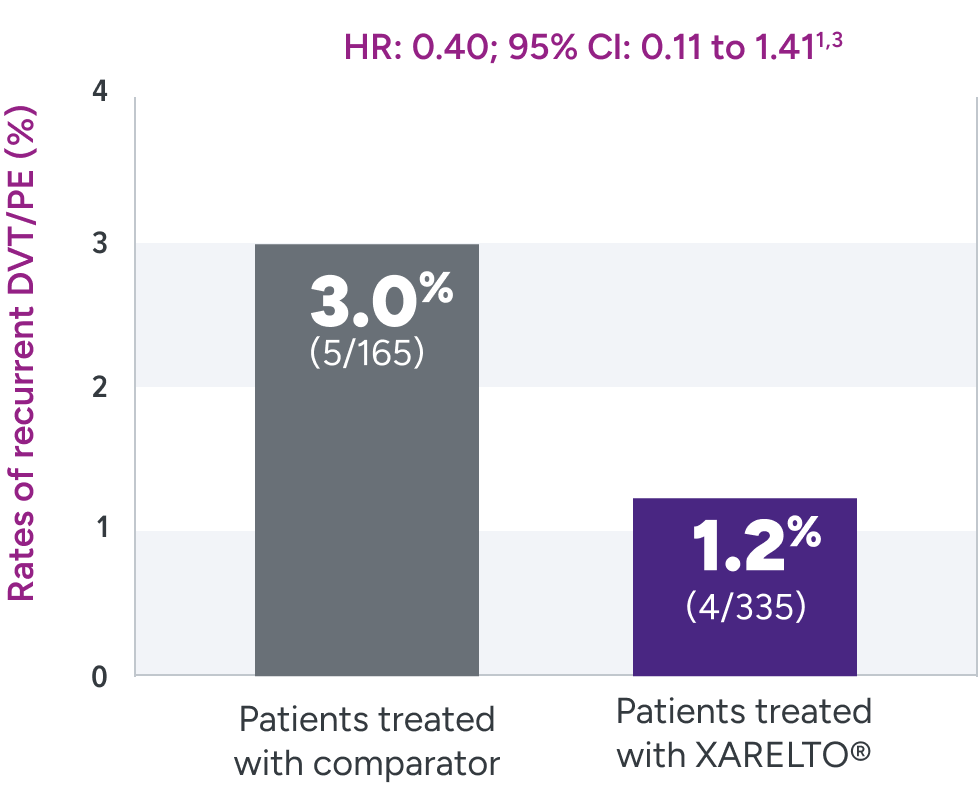
After a median follow-up of 91 days (IQR 87-95) in children who had a study treatment period of 3 months (n=463), and 31 days (IQR 29-35) in children who had a study treatment period of 1 month (n=37).
Other outcomes
XARELTO®
Comparator
Complete Resolution
of index thrombus on
repeat imaging1,3
of index thrombus on
repeat imaging1,3
38%
(128/335)
(95% CI 33.0%, 43.5%)
(128/335)
(95% CI 33.0%, 43.5%)
26%
(43/165)
(95% CI 19.8%, 33.0%)
(43/165)
(95% CI 19.8%, 33.0%)
Secondary Outcome
Symptomatic recurrent VTE
or asymptomatic deterioration
on repeat imaging1,3
Symptomatic recurrent VTE
or asymptomatic deterioration
on repeat imaging1,3
1.5%
(5/335)
(5/335)
3.6%
(6/165)
(6/165)
HR: 0.41
95% CI: 0.12 to 1.36
95% CI: 0.12 to 1.36
Secondary Outcome
Symptomatic recurrent VTE
or major bleeding events1,3
Symptomatic recurrent VTE
or major bleeding events1,3
1.2%
(4/335)
(95% CI 0.4%, 3.0%)
(4/335)
(95% CI 0.4%, 3.0%)
4.2%
(7/165)
(95% CI 2.0%, 8.4%)
(7/165)
(95% CI 2.0%, 8.4%)
Not powered for noninferiority† due to the low incidence of VTE in children and the lack of well-documented information on recurrence and treatment effect with standard anticoagulants in children; hence, there was no formal a priori sample size calculation.3
*
Comparators were given at therapeutic doses, according to international guidelines, and included UFH, LMWH, or fondaparinux. Following completion of 5 to 9 days of standard anticoagulation, participants continued with heparin treatment or were switched to a VKA at the discretion of the treating physician for a main study treatment period of 3 months (or 1 month for children <2 years with CVC-VTE). A diagnostic imaging test was obtained at baseline and at the end of the main study treatment. When clinically necessary, treatment was extended up to 12 months in total (or up to 3 months in total for children <2 years with CVC-VTE).1,3,7
†The study could not be powered to independently show noninferiority for efficacy of rivaroxaban in comparison to standard therapy in children; therefore, interpretation of the results relies in part on extrapolation of data obtained with rivaroxaban in adults; hence, there was no formal a priori sample size.
CI = confidence interval; DVT = deep vein thrombosis; HR = hazard ratio; IQR = interquartile range; PE = pulmonary embolism;
VTE = venous thromboembolism.


