The UNIVERSE clinical trial
The first and only randomized study of a DOAC for use in children with congenital heart disease as thromboprophylaxis post Fontan3
Objective
To examine the use of a novel oral suspension formulation of XARELTO® in children 2 to 8 years old with single ventricle physiology who had the Fontan procedure within 4 months before enrollment2,3
Design2,3
- Randomized
- Multicenter
- Open-label
- Active-controlled
- 2-part (A and B), phase 3 study
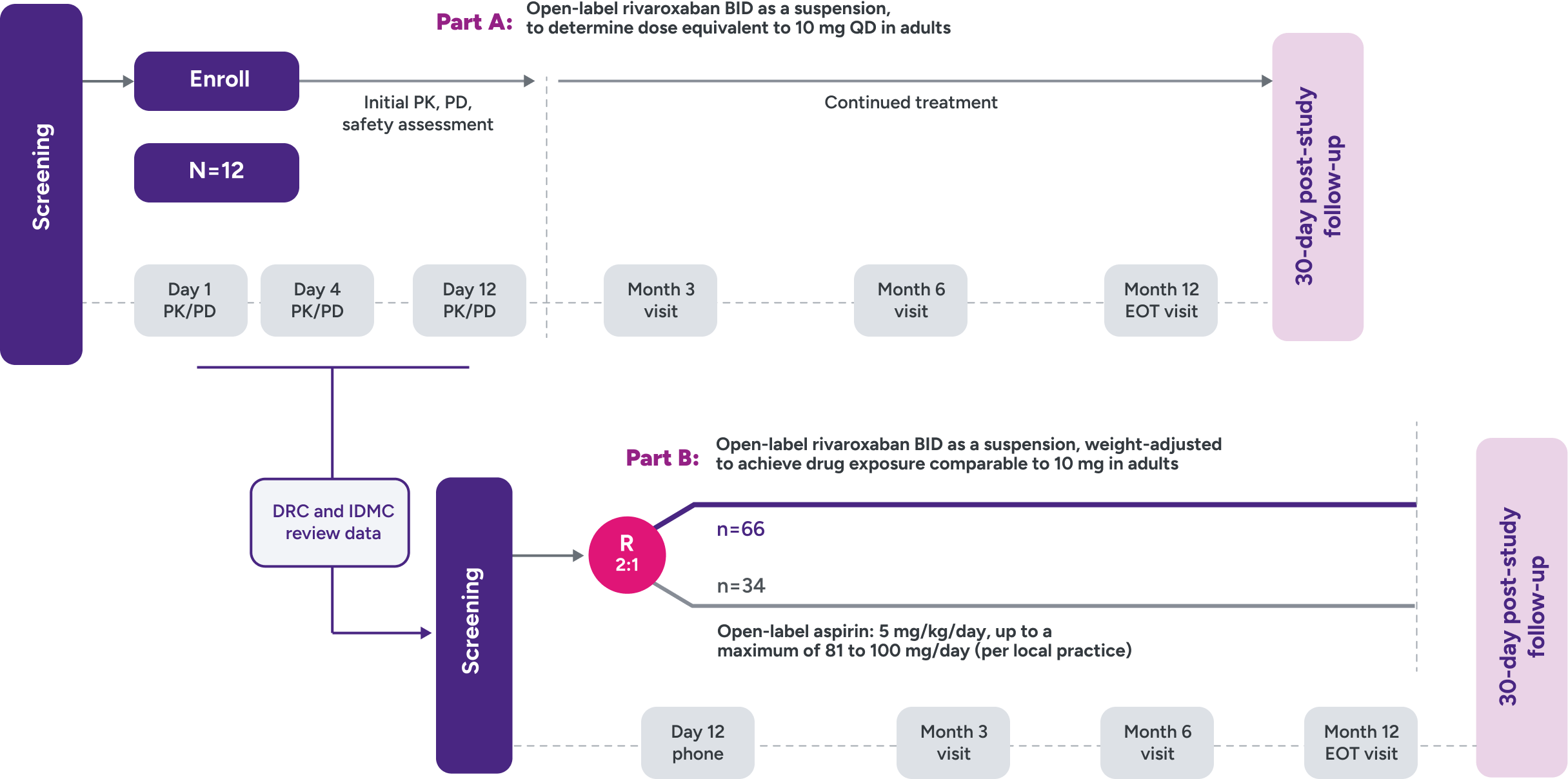
Parts A and B
Part A: Assessed PK and PD of XARELTO® in young children to determine a dose to approximate the drug exposure achieved in adults with XARELTO® 10 mg QD
Part B: Evaluated the safety and efficacy of XARELTO® vs aspirin for thromboprophylaxis post-Fontan procedure for 12 months
UNIVERSE clinical trial study design2,3

Outcomes
Primary efficacy outcome:
any thrombotic event, venous or arterial
Principal safety outcome:
major bleeding events
Secondary safety outcomes:
nonmajor and trivial/minimal bleeding
Inclusion criteria
- Children aged 2 to 8 years with single ventricle
- Within 4 months post-Fontan procedure
Main exclusion criteria
- Thrombosis requiring treatment
- History of GI disease or surgery associated with impaired absorption
- Active, or high risk of bleeding contraindicating antiplatelet or anticoagulant therapy, including history of ICH, or contraindication to aspirin or rivaroxaban
- Chronic NSAID use
- Platelet count <50 x 109/L at screening
- Estimated eGFR <30 mL/min/1.73 m2
Not powered to test formal hypotheses for efficacy and safety due to the limited availability of the study population and the expected low event rates.2,3
R = randomization.
UNIVERSE clinical trial
Bleeding rates were assessed for XARELTO® vs aspirin1
Principal safety outcome
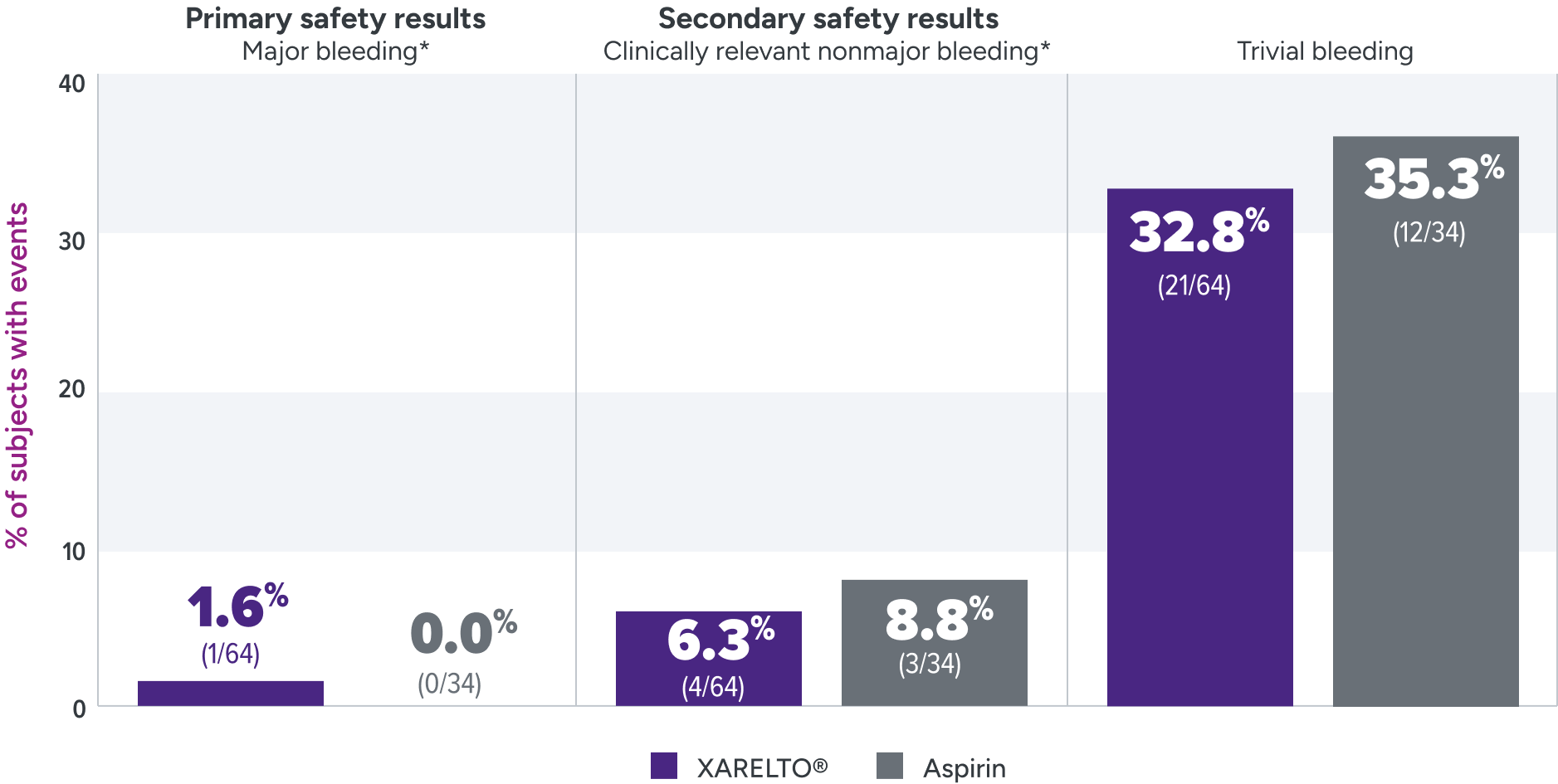
Major bleeding: The single case of epistaxis (nosebleed) occurred in the rivaroxaban part B group.
Clinically relevant nonmajor bleeding: With rivaroxaban, bleeding events occurred in the lower GI tract, gingival tissue, and skin; with ASA, these events occurred in the lower GI tract, skin and subconjunctival tissue, and one patient developed a hematoma.
Trivial bleeding: The most frequent site of trivial bleeding was the skin in both groups.
Not powered to test formal hypotheses for efficacy and safety due to the limited availability of the study population and the expected low event rates.2,3
*Clinically relevant nonmajor bleeding is clinically overt bleeding, which did not meet the criteria for major bleeding but was associated with medical intervention, unscheduled contact with a physician, temporary cessation of treatment, discomfort for the patient, or impairment of activities of daily life. Major bleeding is clinically overt bleeding associated with a decrease in hemoglobin of ≥2 g/dL, a transfusion of ≥2 units of packed red blood cells or whole blood, or bleeding at a critical site or with a fatal outcome.
ASA = aspirin; GI = gastrointestinal.
The UNIVERSE clinical trial was not powered for statistical significance
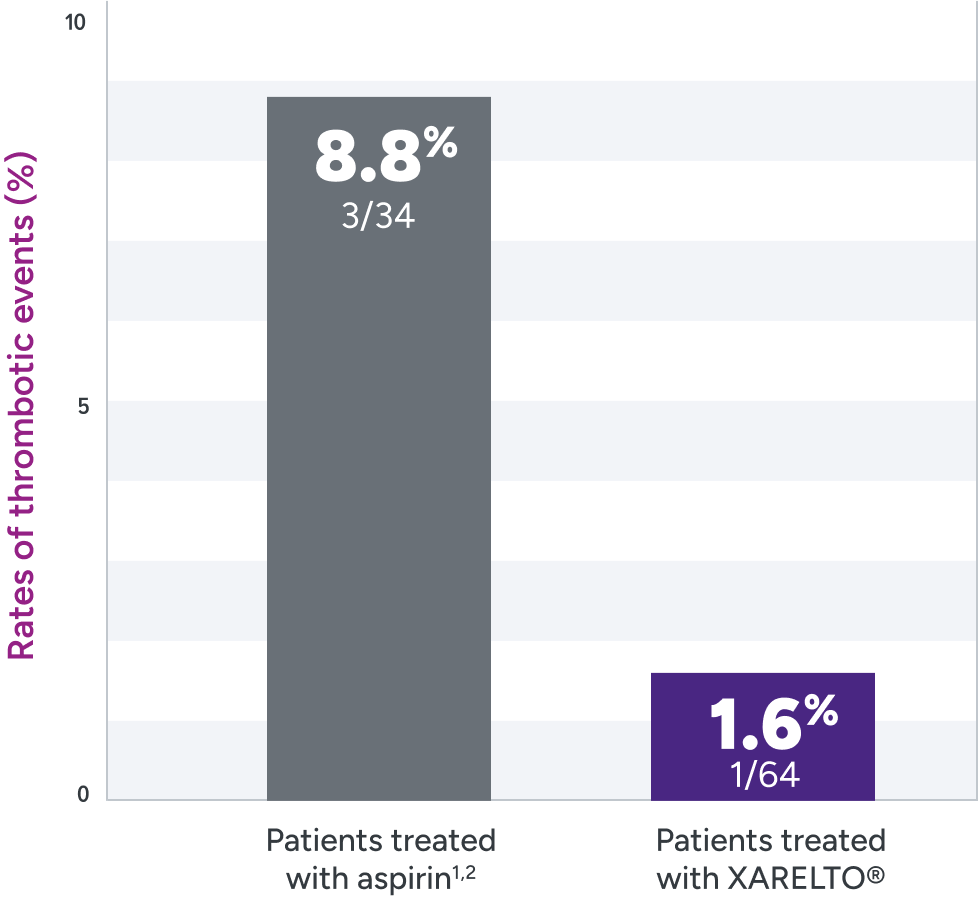
XARELTO® was evaluated for the prevention of thrombotic events in pediatric patients post Fontan2
Rates of primary and secondary efficacy outcomes1,2*
| Event | Treatment arm† | |
|---|---|---|
| XARELTO®‡ n=64% n (%) | Aspirin‡ n=34 n (%) | |
| Primary efficacy outcome | 1 (1.6) | 3 (8.8) |
| Ischemic stroke | 0 | 1 (2.9) |
| Pulmonary embolism | 1 (1.6) | 0 |
| Venous thrombosis | 0 | 2 (5.9) |
Not powered to test formal hypotheses for efficacy and safety due to the limited availability of the study population and the expected low event rates.2,3
*Efficacy outcomes based on full analysis set: all participants in part A who received ≥1 dose of study drug and all participants in part B who were randomized and received ≥1 dose of study drug. In the rivaroxaban part A group, 1 participant (8%) had a venous thrombotic event on Day 362 of treatment (364 days post-Fontan procedure). This study was not powered for efficacy hypothesis testing (post hoc log-rank test; P=0.095).2
†Part B: randomized 2:1 (XARELTO®: aspirin).
‡Treatment schedule: body weight–adjusted doses of XARELTO® (exposures to match that of 10 mg QD in adults) or aspirin (approximately 5 mg/kg).
QD = once daily.


